What Is And What Are The Functions Of The Frontal Lobe Of Our Brain?
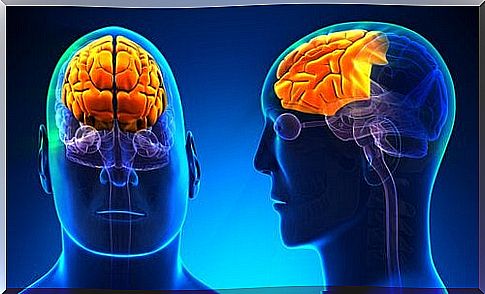
The nervous system is an enormously complex tangle of neurons and glial cells. Ultimately, these are the structures that will determine our behaviors, thoughts and emotions. These nerve units are grouped into larger structures in order to fulfill their functions, and each of these groups will be just a grain of sand in this very complex machine that is our body. One of the most notable structures in the nervous system is the brain, and the brain divides into a series of areas called the lobes. Among the cerebral lobes is the frontal lobe, which will be the protagonists of this article.
First of all, we must understand that lobes are theoretical definitions from the division of the cerebral cortex. This division was carried out according to the role that the parties play in the different processes and by location. We can make an analogy with the Earth: if the brain were the Earth, the wolves would be the continents.
This classification is very functional, as it serves as a map to easily locate certain points on the surface of the brain. The cerebral cortex is composed of 6 functional lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insular and limbic. In this article we will focus on what we could say is the most relevant of them, the frontal lobe. We’ll start by highlighting the area it occupies, since that’s a third of the total area of the cortex.
Frontal lobe structure and functions
The frontal lobe is found in the most anterior part of the brain, more precisely occupying the entire cerebral cortex starting from the central sulcus. It is considered a very important wolf due to the fact that it fulfills central functions in information processing, especially information that has an executive character. Furthermore, we can also say that the frontal lobe is divided into multiple regions that provide it with a wide variety of functions.

When we group the different functional structures of this lobe, we can speak of two major areas. One of them would be the area corresponding to the motor functions, the motor cortex, fulfilling all the functions of movement. The other area would be the prefrontal cortex, in charge of executive processes, decision making and different aspects related to the regulation of emotions.
motor cortex
The frontal lobe motor cortex will be the manager of all the body’s efferent systems. Thanks to it, we will be able to perform all kinds of voluntary motor acts and actions. This structure will be in charge of both planning the movement and transmitting the orders to the muscles for them to take action. It is important to emphasize that this part of the cortex is only responsible for voluntary movements, the involuntary motor system is based on other structures, such as the basal ganglia and the cerebellum.
We can find three relevant sub-areas to be mentioned within the motor cortex.
- The premotor area. It is in charge of planning and programming the movements. Before performing any movement, the neurons in this area are responsible for establishing the muscles and the steps necessary for it to occur correctly.
- The primary motor area. It is the cortical part that is in charge of carrying out the step by step prepared by the premotor cortex. That is, it is in charge of initiating the action of the movement, sending orders to the muscles.
- Broca’s area. It is in charge of language production. Its function is to coordinate the phonological muscles so that the person can speak and pronounce. It is also related to writing production. To learn more about her, click here.
prefrontal cortex
This region is responsible for the executive system and for processing information in the human brain. The frontal lobe’s prefrontal cortex is the ultimate basis for human cognition, behavior, and emotional response. It is the mediating part among many other structures that are distributed throughout the brain, playing a key role in decision-making.
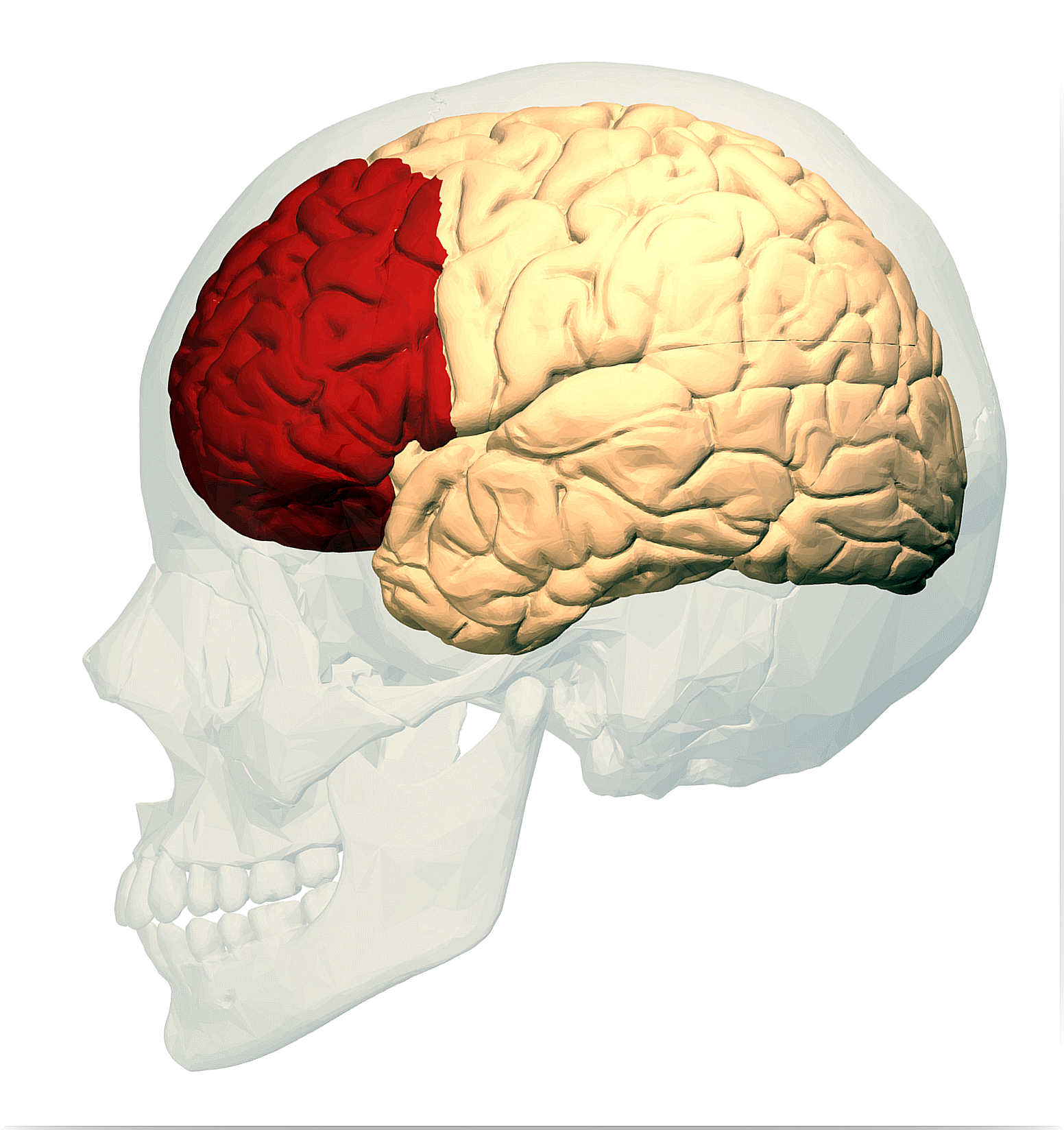
We cannot fail to mention that executive functions are a set of higher-order cognitive abilities that control our behavior and emotions. Otherwise, we can say that all those processes that deal with managing, organizing, coordinating and directing are carried out in this area. It could be described as the processor of a computer if we were to make a comparison with these machines.
Within this cortical area we can distinguish three regions of great functional importance:
- The dorsolateral frontal cortex. Region connected with other locations of other wolves that transforms thinking into plans, behaviors and decisions. The dorsolateral frontal cortex is closely related to higher psychological processes such as working memory, metacognition, attentional control, cognitive flexibility, etc.
- The cingulate area. Its functions are highly related to the regulation of motivational processes. It is responsible for inhibiting or inciting action in the individual. It is also in charge of certain processes related to the regulation and support of care.
- The orbitofrontal cortex. Fulfills the mission of controlling affectivity and social behavior. It takes part in the processing and regulation of emotions and affective states, adapting behavior depending on the context.
The frontal lobe is one of the most relevant structures within our brain. Its study, through various neuroscientific techniques, gives us very valuable information: understanding its structure and functionality brings us closer to understanding our biology and gives us clues about its relationship with our behavior, emotions and thoughts.









